40
Intramuscular administration of drugs
In intramuscular injection drugs are introduced into the muscle layer, lo-
cated below the subcutaneous fat. Muscles are less sensitive than skin and sub-
cutaneous fat. The drugs injected into them are absorbed faster due to more
blood vessels number and muscle contraction. Many drugs may be adminis-
tered intramuscularly that are available in solutions and do not cause irritation
of soft tissues. If injections are necessary, the place of administration of the drug
should be changed and registered. That reduces the likelihood of a local tissue
reaction and improves drug absorption.
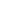
Intramuscular injection can be performed in the shoulder area (deltoid mus-
cle), in the middle third of the anterolateral surface of the hip (wide lateral hip
muscle) and in the buttocks (upper external quadrant of the buttock). The glu-
teal area is divided into 4 parts. Intramuscular injection can be done only in the
upper outer quadrant. The injection can not be done to the upper interior quad-
rant, as most of the quadrant is the sacrum, and the muscle layer is very small.
In the lower interior quadrant there are large artery, vein and sciatic nerve, in the
lower outer quadrant it is occupied the head of the femur (Fig.20).
Fig. 20. Place of intramuscular injection
Algorithm for performing intramuscular injection
1. Determine the injection place.
2. Treat the injection place site 10
×
10 cm alcohol ball using movements
from the center to the periphery.
3. Treat the injection site 5
×
5 cm with another ball with disinfection alcohol,
using the movement from the center to the periphery.