12. Развитие костной ткани из мезенхимы
(прямой остеогенез)
(гематоксилин – эозин)
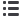
На препарате поперечный срез нижней челюсти
зародыша животного. Челюсть – плоская кость и по-
этому образуется путѐм прямого остеогенеза.На фо-
тографии видим
мезенхиму (2)
и
трабекулы обра-
зующейся кости (1),
окрашенные в ярко-розовый
цвет.Возле формирующейся кости находится
крове-
носный сосуд (3)
– результат васкуляризации скеле-
тогенного островка.
Остеобласты(4)
расположены на поверхности
костной балки, имеют полигональную форму ирезко
базофильную цитоплазму.
Остеоциты (5)
находятся в
глубоких слоях трабекулы, где заключены в костные
лакуны.
Остеокласты (6),
как и остеобласты, нахо-
дятся на периферии трабекулы, при этом являются
крупными многоядерными клетками с оксифильной
цитоплазмой.Разрушая костное вещество,они вне-
дряются в трабекулу, образуя в ней углубления.
12. Development of bone tissue
from the mesenchym (direct osteogenesis)
(hematoxilin-eosin)
The cross-section of the lower jaw of the embryo
of the animal is presented in microscopy slides. The
jaw is a flat bone and is therefore formed by direct os-
teogenesis. In the photo we see
the mesenchyme
(2)
trabeculae of
the bone (1)
, colored in bright pink.
Near the forming bone the
blood vessel (3)
is situated
as the result of vascularization skeletogenesis island.
Osteoblasts (4)
are located on the surface of the
bone trabecula, have a polygonal shape and sharply
basophilic cytoplasm.
The osteocytes (5)
are located
in the deep layers of the trabeculae, which concluded
in the bone lacunae.
Osteoclasts (6)
, as well as os-
teoblasts, are on the periphery of the trabecula, while
they are large multi-core cells with oxyphilic cytop-
lasm. Destroying bone substance, they are imple-
mented into the trabecula, forming hollows in it.
28